The Enigma of Antarctica
Antarctica is a land of extremes—barren, frozen, and cloaked in intrigue. Beneath its icy surface lie unexplained structures and evidence of ancient cosmic collisions, including a massive crater that challenges our understanding of Earth’s history. Chinese scientists have uncovered findings that defy conventional knowledge, igniting global debate and capturing the attention of figures like Joe Rogan. From ancient anomalies to urgent environmental warnings, these discoveries are reshaping our view of Earth’s coldest frontier. What secrets are hidden beneath the ice, and why are they so closely guarded?
China’s Strategic Antarctic Ambitions
China’s Antarctic journey began in 1980 with an invitation from Australia to explore the icy continent. By 1984, China launched its first expedition, swiftly establishing itself as a major player alongside nations like the US and Russia. In 1985, they built the Great Wall Station on King George Island, a wind-battered hub in the South Shetland Islands, followed by the Zhongshan Station on the eastern coast, accessing remote terrains. These stations serve as both scientific outposts and geopolitical markers.
China’s diplomatic strategy was equally calculated. By joining the Antarctic Treaty System and securing consultative party status in 1985, they gained voting rights in Antarctic policymaking. Early research at Great Wall Station explored atmospheric whistlers—electromagnetic waves offering insights into space weather—while Zhongshan Station focused on geomagnetism, ocean currents, and krill populations. These foundational studies, though understated, laid the groundwork for major breakthroughs. China’s rapid rise and reserved nature have sparked speculation about their true objectives beneath the ice.
The Penguin Guano Breakthrough
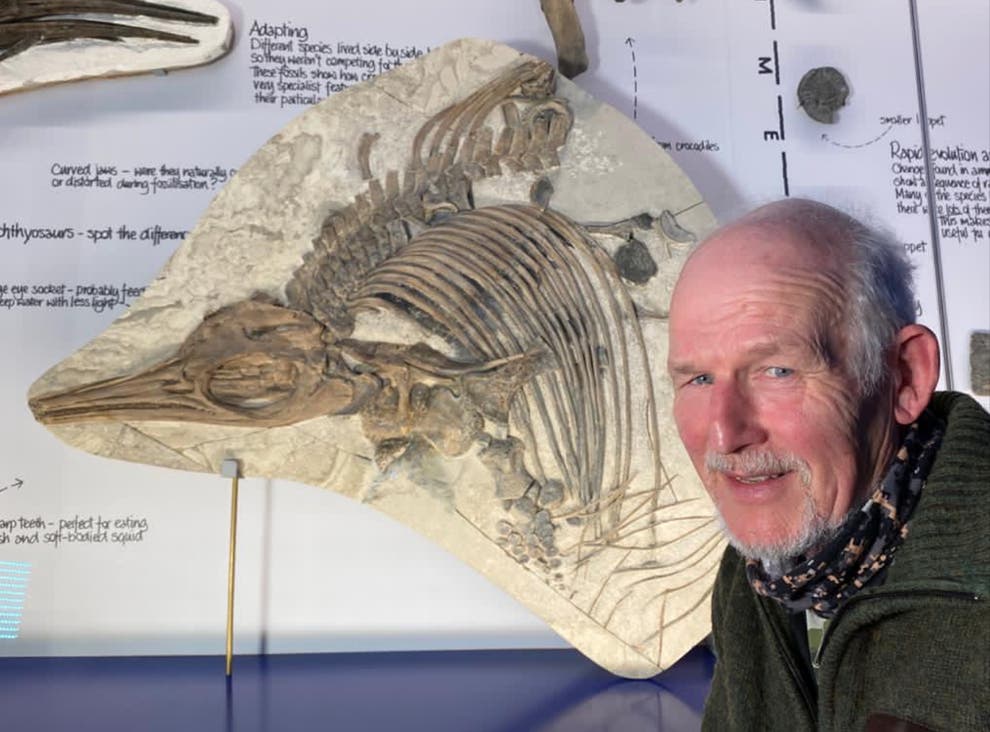
In 2000, Chinese geochemist Sun Liguang published a landmark study in Nature, unlocking a 30,000-year climate record through penguin guano. By analyzing chemical markers like phosphorus and copper in layered droppings near coastal penguin colonies, Sun’s team reconstructed population trends tied to climate shifts. Warmer periods boosted krill and fish, increasing penguin numbers, while colder phases disrupted food chains, causing declines. This discovery provided a biological timeline of ecological change, delivering critical data for climate models during heated global warming debates. Penguin guano became a powerful climate indicator, elevating China’s status in polar research.
Ice Cores: Earth’s Climate Time Capsule
At Dome Argus (Dome A), Antarctica’s highest and coldest point, China embarked on an ambitious project starting in 2004 to drill ice cores—frozen records of Earth’s atmosphere. Overcoming temperatures as low as -58°F, they extracted a 108-meter core in 2004, an 800-meter core by 2009, and a groundbreaking 200-meter ice and subglacial core in 2019 using custom-built equipment. These cores, containing ancient air bubbles, dust, and volcanic fallout, revealed climate swings and CO2 spikes over millennia, confirming rapid historical sea level rises. Subglacial samples illuminated ice-rock interactions, critical for predicting glacier stability and coastal flooding risks. China’s technological and scientific prowess underscores the geopolitical weight of these findings.
The Gamburtsev Mountains: Geological Revelations
Beneath nearly two miles of ice, the Gamburtsev Mountains—dubbed the “ghost mountains”—lie hidden in East Antarctica. In the 2000s, Chinese scientists used ground-penetrating radar and seismic imaging to map this ancient range, uncovering alpine valleys shaped by tectonic forces over a billion years ago. These findings revealed Antarctica’s dynamic geological past and its modern implications: the mountains’ structure could accelerate ice melt as the continent warms, hastening sea level rise. This discovery, vital for global climate models, highlights China’s role in uncovering Earth’s hidden frameworks.
Joe Rogan’s Antarctic Fascination
Joe Rogan’s podcast, The Joe Rogan Experience, has repeatedly explored Antarctica’s mysteries. In episode 1,429, adventurer Colin O’Brady recounted his solo 932-mile trek across the continent, describing its eerie isolation. Episode 1,996 with Navy SEAL Andy Stumpf highlighted Antarctica’s brutal conditions, from crevasses to intense UV exposure. In episode 2,136, historian Graham Hancock discussed ancient maps suggesting an ice-free Antarctica, while comedian Sam Tripoli speculated about Operation High Jump’s secretive motives. Rogan’s curiosity—why the intense global focus on a desolate continent?—echoes questions about China’s strategic research efforts.
Global Impact: A Climate Wake-Up Call
China’s Antarctic discoveries have transformed climate science. The penguin guano study linked ecosystem shifts to sea ice and ocean changes, while ice cores revealed abrupt climate swings, warning of rapid sea level rise. The Gamburtsev Mountains showed how geological structures influence ice melt rates. Through initiatives like CAREA (2012) and the Inexpressible Island station, China monitors ice, oceans, and ecosystems, sharing data globally. These findings, published in major journals, aren’t hidden secrets but urgent warnings. The timeline for climate change is measured in ice melt rates and ecological shifts, urging humanity to act swiftly on China’s data to avert catastrophic scenarios.